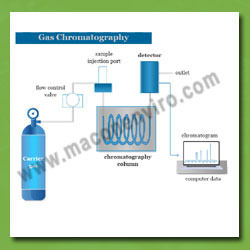
Gas Chromatography
We Macon Enviro Technologies as engaged in Manufacturers, Suppliers, Provider, Installation, Commissioning, Consultant Gas Chromatography. Gas chromatography (GC) is a widely used analytical technique for separating and analyzing volatile compounds. It is based on the principle of partitioning a sample between a mobile phase (carrier gas) and a stationary phase (a high-boiling liquid or solid adsorbent). The mobile phase carries the sample through a column, while the stationary phase retains certain components more strongly than others, leading to separation. The sample, which can be in liquid or gaseous form, is introduced into the GC system. For liquid samples, they are usually injected using a syringe into a heated injection port. The injection port quickly vaporizes the sample, converting it into its gaseous phase. A carrier gas, such as helium or nitrogen, is used as the mobile phase. The carrier gas flows through the system and carries the vaporized sample into the column. The choice of carrier gas depends on the analyte's properties and the specific requirements of the analysis. The column is packed or coated with a stationary phase material. The stationary phase can be a solid material (stationary phase adsorption chromatography) or a liquid film immobilized on a solid support (stationary phase partition chromatography). The choice of stationary phase depends on the analyte's characteristics and the separation goals. As the sample enters the column, different compounds in the sample interact differently with the stationary phase. The analytes are partitioned between the mobile and stationary phases based on their affinity for the stationary phase. Components that have a higher affinity for the stationary phase will be retained longer in the column, leading to separation.
As the separated components elute from the column, they enter a detector. The detector measures the concentration of the analytes and produces an output signal, typically in the form of a chromatogram. Different types of detectors can be used, such as flame ionization detector (FID), thermal conductivity detector (TCD), electron capture detector (ECD), or mass spectrometer (MS). The choice of detector depends on the analytes being analyzed and the desired sensitivity and selectivity. The generated chromatogram is analyzed to identify and quantify the components present in the sample. This is typically done by comparing the retention times of the peaks in the chromatogram with those of known reference standards. The area under the peaks can be used to determine the relative concentrations of the components. Gas chromatography is widely used in various fields, including environmental analysis, pharmaceuticals, forensics, food and beverage industry, and petrochemical analysis. It offers high separation efficiency, sensitivity, and versatility, making it a powerful tool for chemical analysis. We at Macon Enviro Technologies are committed to providing a large selection of Gas Chromatography to our esteemed clients In Mumbai, Navi Mumbai, Thane and around India.